Blockchains such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, TRON, etc. all work independently. Each has its own setup, token rules, and agreement methods. You can't directly send crypto from one blockchain to another.
For instance, you can't send USDT from Ethereum (ERC-20) to a TRON (TRC-20) wallet directly. To do that, you need something that can move crypto between blockchains. One of it is a blockchain bridge.
So, how do tokens really move between networks? What role do bridges play in these transactions? Let's take a look at how it all works.
How Blockchains Work in Cryptocurrency
A blockchain is a digital record book that tracks every transaction on its network. Each record is linked to the previous one. It creates a secure and permanent chain. Their consensus mechanisms (like Proof-of-Work for Bitcoin or Proof-of-Stake for Solana) ensure that no record can be deleted or changed.
Each blockchain operates on its own with its own unique settings:
- Its own chain ID
- Different address styles for wallets and transactions
- Unique smart contract designs
- A specific way of agreeing on things (like miners in Bitcoin or validators in Solana)
Most blockchains also create their own tokens, which power their systems and allow different things to be done:
- TRX in the TRON network
- BTC in Bitcoin
- ETH in Ethereum
- SOL in Solana
What is moving crypto between blockchains?
Moving crypto to another blockchain is really just a cross-chain token transfer. If you do this, you can use tokens from one blockchain on another. But you have to use certain ways to make it happen.
There are three main ways to transfer crypto between networks:
- Swap via router (DeFi exchange).
The user sends tokens to a liquidity pool and receives wrapped tokens in the target network. For example, ETH from Ethereum is exchanged for wETH on Polygon. - Token wrapping.
The original asset is locked by a service provider, and an equivalent wrapped token is minted on the target chain. This is how wBTC (Bitcoin wrapped on Ethereum) operates. - Atomic swaps through smart contracts.
An automated process where smart contracts ensure either the full completion of a transaction or its refund if any part fails.
Every cross chain transfer crypto process involves transaction fees — often called gas fees — that depend on the network’s capacity and confirmation time.
What Are Blockchain Bridges?
Blockchain bridges are services or protocols that enable crypto transfer networks to communicate with each other. In essence, they link otherwise isolated blockchains, allowing users to move tokens to another chain seamlessly.
Bridges serve several core functions:
- Transaction routing between ecosystems
- Liquidity management across pools and providers
- Support for multiple blockchain protocols
- Verification of cross-chain transactions via validators and oracles
- Transparency through on-chain explorers, where every hash and confirmation can be verified
Here’s a simple scenario. Suppose you want to send USDT from Ethereum to TRON. On a centralized exchange, this would require multiple steps — deposits, conversions, and withdrawals. Using a bridge automates this process: your Ethereum USDT gets locked, and the equivalent amount is released on TRON.
How Cross-Chain Transfers Work: Bridges and Swaps
Both bridges and swap services help users transfer network crypto across blockchains — but in different ways.
A swap is a token exchange that happens through a smart contract or decentralized exchange (DEX). For instance, you can trade ETH for USDT within the same blockchain. However, when moving tokens between networks, swaps alone are not enough.
A bridge operates differently. When someone starts a crypto transfer between chains, the system holds their crypto on the original chain. Then, it creates matching tokens on the destination chain and sends the transfer through available liquidity pools. Validators verify the transfer, gas fees are calculated, and the transaction is finalized after the required confirmations.
Ways to Transfer from One Blockchain to Another
There are several ways to transfer crypto between networks depending on your goals and risk tolerance:
- Centralized exchanges.
Think of these exchanges as a bank for crypto. You can put your crypto in, and when you take it out, you can use a different network. - Cross-chain bridges.
These are like direct routes for your crypto between different blockchains, cutting out the middleman. They let you move your assets from one blockchain to another. - DeFi protocols and routing aggregators.
These platforms combine liquidity from multiple sources and automatically choose the most efficient route for your cross chain transactions. - Atomic swaps.
Two users exchange assets from different chains directly through smart contracts — without relying on any third party.
When to Use Cross-Chain Bridges — and How They Work
Cross-chain bridges are great for people who want options when handling their assets and getting into different blockchain systems. They work well if you need:
- Fast transfers without centralized intermediaries
- Low transaction costs
- High network throughput
- Full control over your funds via decentralization
Here’s how a cross chain token transfer typically works:
- The user sends crypto to a bridge address on the source chain.
- Validators and oracles confirm the transaction.
- The assets are locked in the original blockchain.
- Equivalent wrapped tokens are minted in the target network.
- When reversed, wrapped tokens are burned and the original funds are unlocked.
How to Bridge Crypto in Crypto Office
The Crypto Office service simplifies cross chain transfer crypto operations and allows users to exchange assets between networks directly inside Telegram. Unlike complex third-party bridges, the system automates every technical step — users only provide transfer parameters.
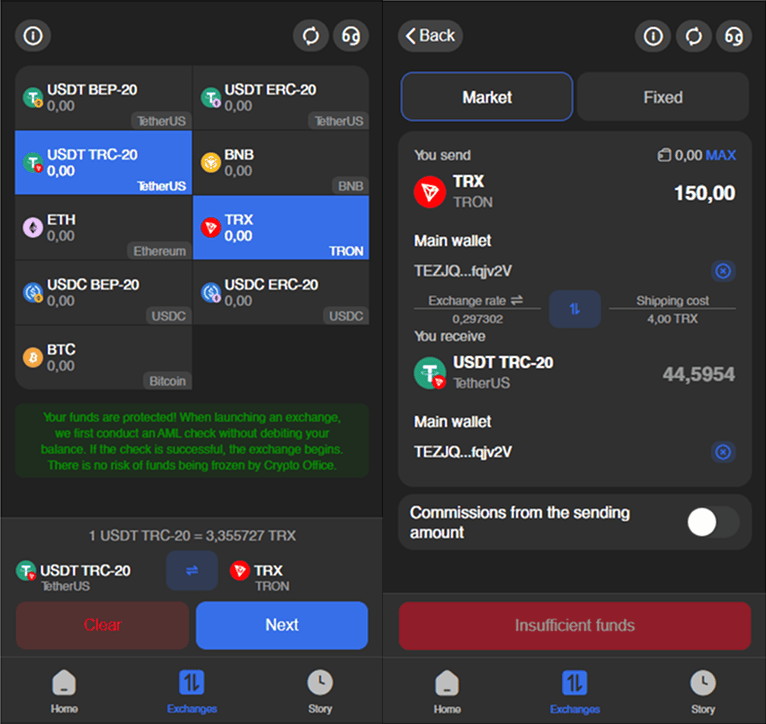
Step 1 – Choose tokens for exchange
Select the cryptocurrency you want to send and the token you wish to receive. The bot will display available pairs.
Step 2 – Enter amount and recipient address
Specify the transfer amount (for example, TRX) and the wallet address for the desired network (for example, USDT BEP-20).
Always double-check both addresses and network types — mistakes may lead to a wrong network crypto transfer.
Step 3 – Confirm and pay
Choose the exchange rate type — “Market” or “Fixed.”
Verify the final details: rate, network, wallet, and fees.
Once confirmed, Crypto Office automatically performs AML screening and launches the cross chain crypto transfer.
Step 4 – Receive funds
After confirmation, your converted tokens will appear in the chosen wallet within seconds.
Crypto Office handles liquidity management, routing, security, and finalization, ensuring that users can transfer crypto between networks quickly and safely.
What Affects the Cost of Cross-Chain Transactions
The price of a crypto transfer network depends on several variables:
- Gas fees. Each blockchain requires payment to miners or validators. Ethereum’s gas prices are often higher than those of TRON or BNB Smart Chain.
- Network load. When blockspace is busy, fees rise and confirmations take longer.
- Bridge or provider type. Centralized bridges and exchanges may charge service fees, while decentralized ones take a portion for smart-contract execution and liquidity-pool usage.
- Routing and conversion path. Some assets pass through intermediate chains, which can affect cost and confirmation speed.
- Limits and quotas. Many bridges have minimum or maximum amounts for each cross chain token transfer, influencing user convenience.
Crypto Office, for example, figures out all the costs for you and shows them upfront, so everything's clear.
Popular Bridges and Ecosystems for Cross-Chain Transfers
There are many tools and DeFi setups that can help you move tokens to another chain fast. Some popular choices are:
Ethereum L2 Ecosystems: Arbitrum, Optimism, Base
These networks use roll-up tech to scale Ethereum and keep fees down.
- Arbitrum and Optimism Bridges allow users to move ETH and ERC-20 tokens between chains with low gas fees.
- Base Bridge, created by Coinbase, is an easy way to move crypto across chains straight into the Base ecosystem.
Moving your crypto back to Ethereum can take anywhere from a few minutes to a couple of hours. This is because of the confirmation process which keeps your transactions secure.
Multi-Chain Ecosystems: Polygon, BSC, Solana, Avalanche
These networks all vie for users by offering low fees and fast transaction speeds.
- Polygon Bridge links Ethereum and Polygon, wrapping ERC-20 assets so they’re cheaper to use.
- Binance Bridge makes cross-chain transactions between BNB Smart Chain and other networks easier.
- Jupiter (Solana) finds the best way to move liquidity between Solana, Ethereum, BSC, Avalanche, and others.
- Avalanche Bridge connects Ethereum and Avalanche, giving you high speed and low fees.
All these bridges are the basis for today's cross-chain crypto transfer setup, making it easy to move liquidity around different blockchains.
Security When Moving Tokens Between Networks
Every cross chain transfer crypto involves some risk. To minimize it, follow these practices:
- Use trusted bridges and platforms with transparent code, strong liquidity, and an established reputation.
- Double-check addresses and chain IDs before every crypto transfer wrong network mistake can result in permanent loss.
- Track transactions through blockchain explorers — such as Tronscan.org, Etherscan.io, Solscan.io, and Bscscan.org — to confirm hash, block, and status.
- Avoid fake or phishing websites. Always verify URLs before connecting wallets.
- Protect private keys and seed phrases; for large amounts, rely on hardware wallets.
Crypto Office enhances safety by automating routing, pre-calculating fees, and using transparent cross chain transactions verified in real time.
The Future of Cross-Chain Connectivity
Cross-chain tech is changing DeFi by letting you play around in different ecosystems. This helps cut costs and puts all sorts of DeFi tools from different blockchains at your fingertips.
As more systems adopt common interop standards, transferring crypto across networks should become faster and simpler. Cross-chain bridges can act as connectors for different blockchains, rollups, and sidechains, integrating them into a unified crypto system.
Conclusion
Cross-chain tech lets you move tokens across different networks super fast and easy. Forget those complicated manual steps—now it's done in seconds.Whether you’re bridging ETH to BSC or transferring USDT between TRON and Ethereum, the process has never been more streamlined.
Crypto Office gives users total control of their digital currency, clear fees, and fast multi-chain access. It's built to be the simplest and safest way to move crypto across different networks right now.